Reasons as to Why is Lake Nakuru National Park Famous?
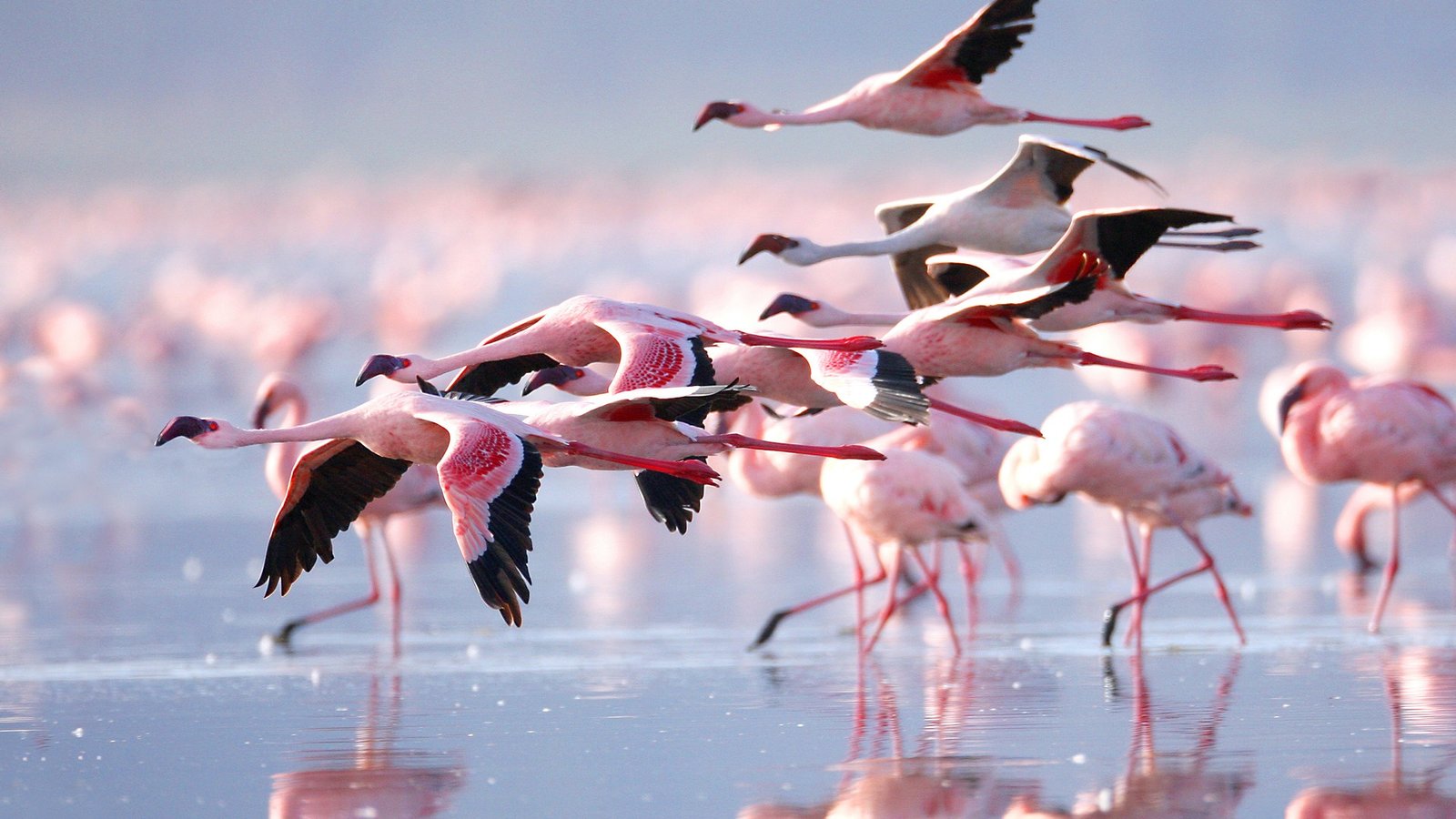
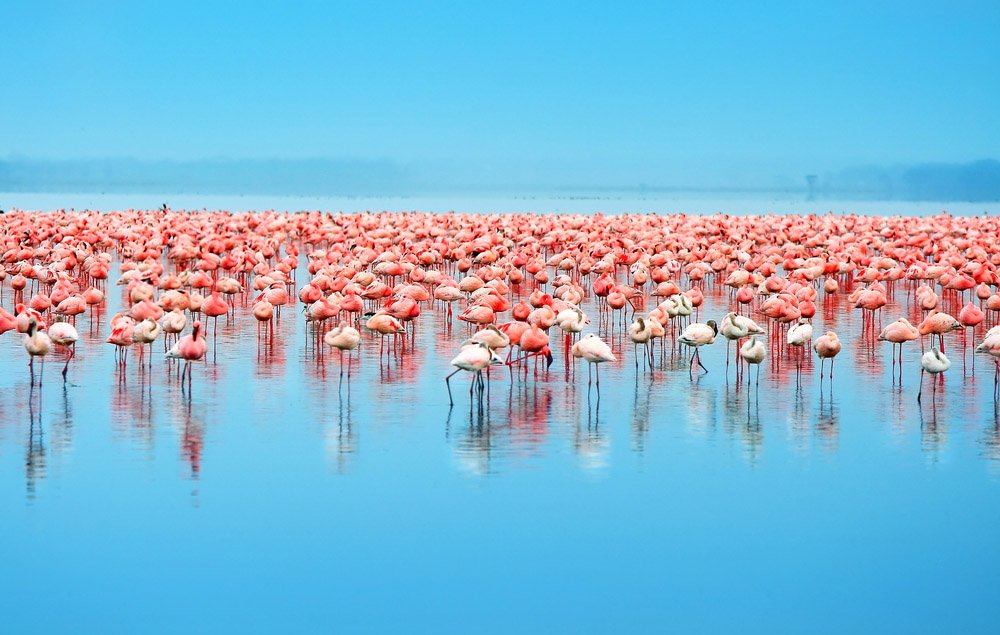
Lake Nakuru National park is located in Central Kenya, about 140km Southwest of Nairobi and lies in the South of Nakuru town in the rift valley of Kenya. The park was established in 1961 and was originally protected as a bird sanctuary. This park was also the first national Rhino sanctuary and hosts one of the largest concentrations of black rhinoceros in Africa and the world. Lake Nakuru, found in the middle of the park occupies about a third of the National park and is surrounded by an ecosystem of wooded and bushy grasslands. The park is famous for thousands of flamingos that hang around the lake. The highly saline nature of the lake supports the abundant growth of algae which is the main food source for the flamingos, therefore, attracting a vast flock together with pelicans that famously nestle around the shore. During the peak season, these birds reach up to 2 million in number and attract about 300 million tourists who travel from all over the world annually to majorly experience this beauty. The baboon cliff gives the best viewpoint for the birds and other wildlife species in the park. It is estimated that the flamingo population consumes about 250,000 kilograms of algae per hectare of surface area per year.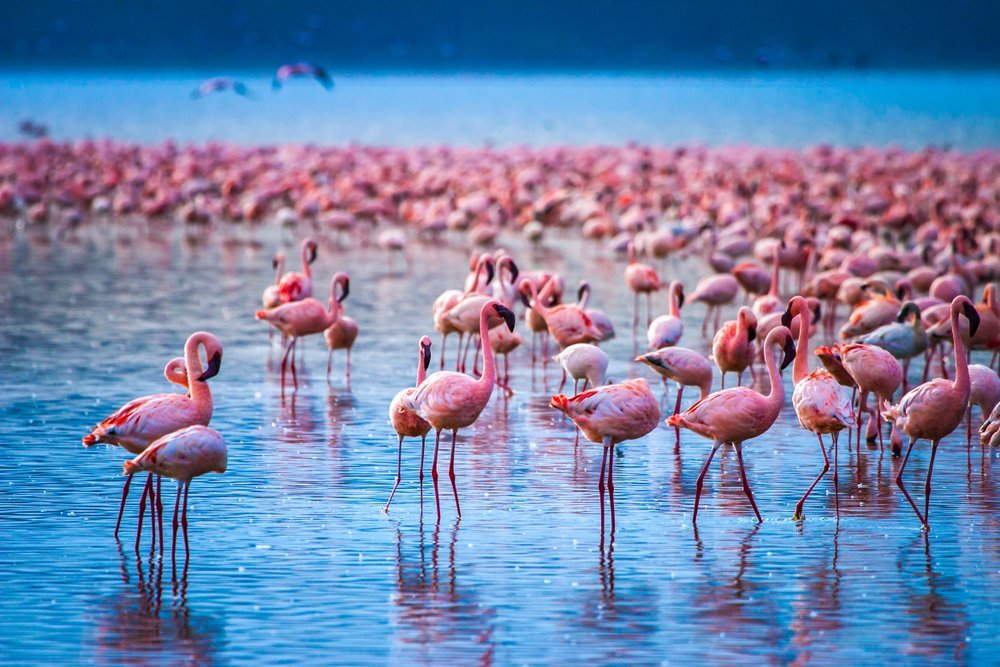
About Flamingos
Flamingos are a large family of brilliantly colored warding birds in the family Phoenicopteridae and inhabit alkaline and saline lakes and lagoons. They prefer to live in hot dry regions, avoiding cool moist forested areas; except in the Andes where they are found on freezing alkaline lakes 14000ft (4250m). Regularly swim, upend and fly with their necks extended. In Africa, two flamingo species exist and both are present in Lake Nakuru National Park;Greater flamingos

Lesser flamingos
The Phoeniconaias minor is the smallest and most numerous species of flamingos. They have a pinkish white plumage and live on the shores of alkaline lakes and lagoons. Most flamingos feed on filtering small or microscopic plant life from mud and water. Lesser flamingos feed on the surface and can feed equally when swimming or walking as long as the water is calm: they don’t feed in rough water. Flamingos prefer to breed on soft mud on which they built characteristic molts usually 6 to 18 (15-46cm) high, shaped like truncated cones with a hollow opening at the top.