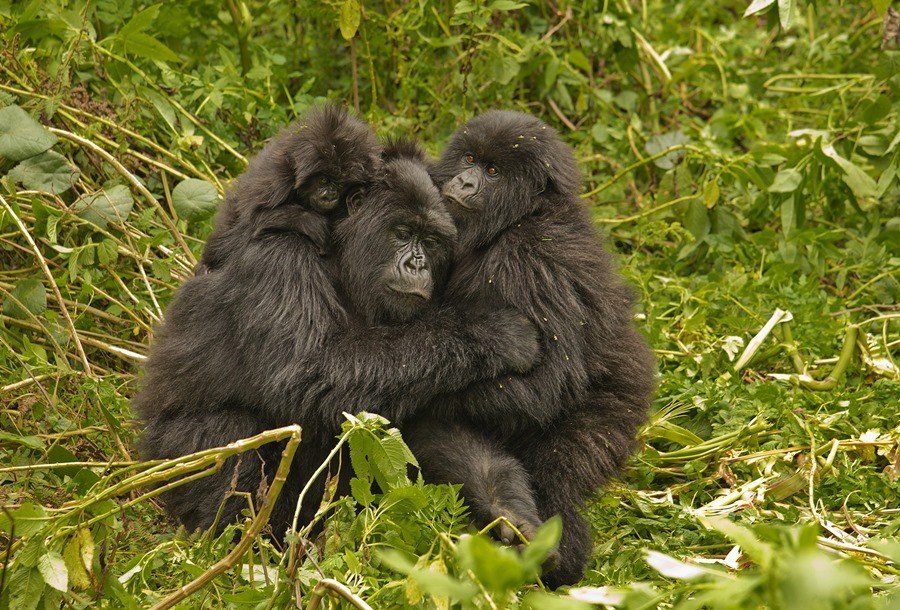
- Mountain Gorilla Conservation: Bwindi is home to approximately half of the world’s remaining mountain gorillas. With over 400 individuals in multiple gorilla groups, it represents one of the most significant habitats for these majestic creatures. Visitors have the opportunity to embark on guided gorilla trekking experiences, allowing them to observe these gentle giants in their natural habitat.
- Ancient Rainforest: The park is characterized by its ancient rainforest, which is estimated to be over 25,000 years old. The dense vegetation, interlaced with thick undergrowth, gives Bwindi its “impenetrable” reputation. This unique ecosystem harbors an incredible variety of plant and animal species, making it a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
- Avian Richness: Bwindi Impenetrable National Park boasts an impressive avian diversity, with over 350 species recorded within its boundaries. Among them are 23 Albertine Rift endemics, making it a haven for birdwatchers. Notable bird species include the African Green Broadbill, Grauer’s Rush Warbler, and the African Emerald Cuckoo.
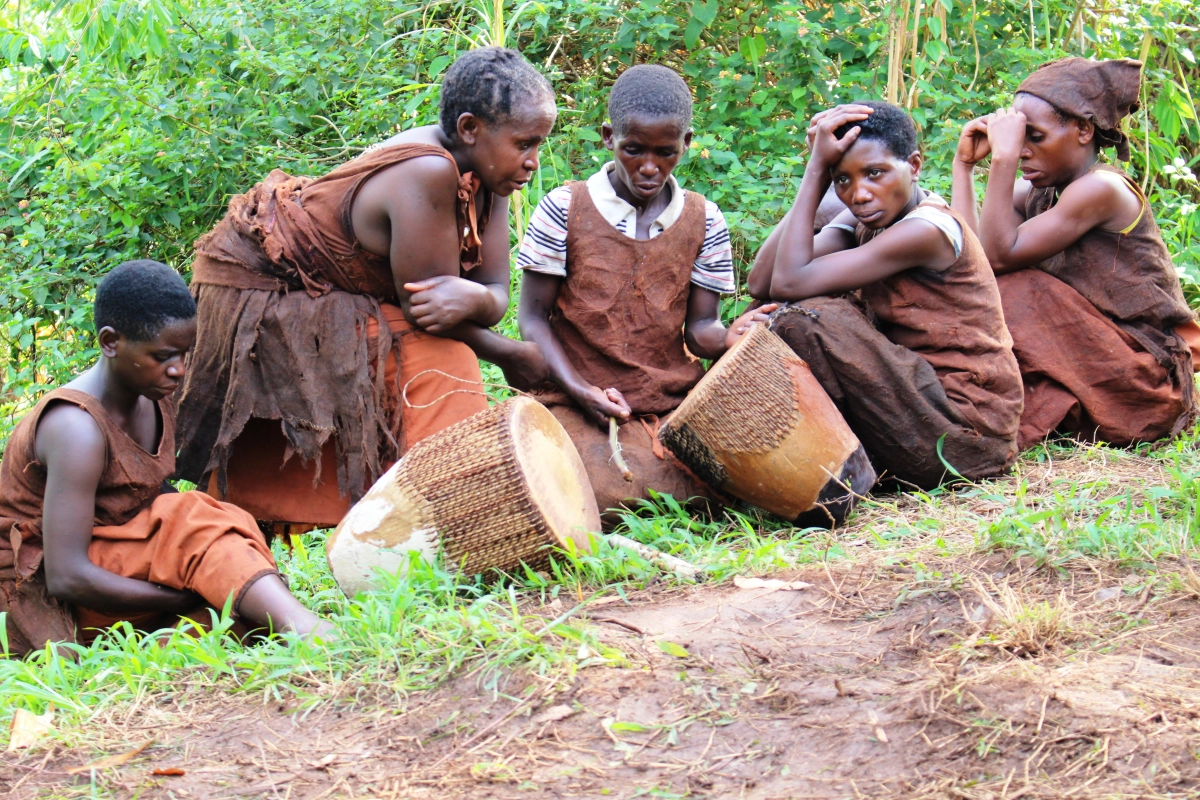

Nature and Culture in Bwindi national park - Cultural Encounters: The park is also home to several local communities, including the Batwa pygmies, who have lived in the forest for generations. Guided community walks and cultural performances provide visitors with the opportunity to learn about their traditional ways of life, their deep connection to the forest, and the conservation challenges they face.
- Conservation Initiatives: Bwindi Impenetrable National Park is at the forefront of conservation efforts to protect the mountain gorillas and their habitat. Various initiatives focus on anti-poaching measures, community engagement, research, and ecotourism. These efforts contribute to the survival and well-being of the gorillas while providing sustainable livelihoods for local communities.
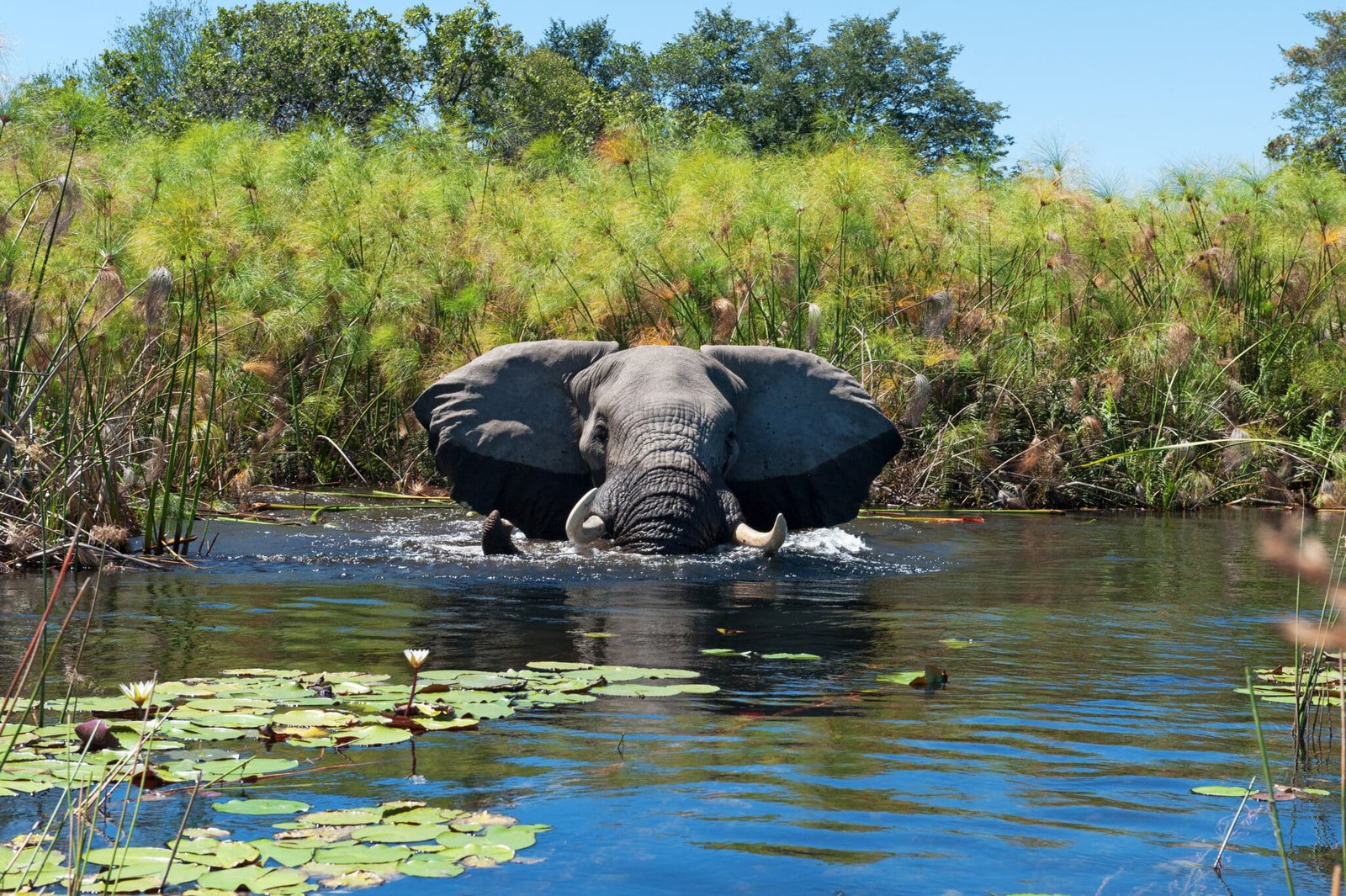
- Biodiversity Hotspot: Beyond the mountain gorillas, Bwindi supports a remarkable array of flora and fauna. The park is home to 120 mammal species, including chimpanzees, elephants, and several primate species like the black-and-white colobus monkeys and L’Hoest’s monkeys. The forest harbors numerous plant species, including rare and endemic orchids.
- Gorilla Habituation Experience: In addition to the regular gorilla trekking, Bwindi offers a unique Gorilla Habituation Experience. This special activity allows visitors to spend an extended period with a gorilla group undergoing habituation, providing a more immersive and educational encounter with the gorillas.
- Batwa Pygmies: The Batwa people are indigenous hunter-gatherers who have inhabited the forests around Bwindi for generations. They have a deep connection to the forest and possess an intimate knowledge of its resources. Despite facing numerous challenges, efforts have been made to preserve their cultural heritage, and visitors have the opportunity to engage with Batwa communities and learn about their traditional way of life.
- Traditional Practices: The Batwa and neighbouring communities have distinct cultural practices that have been passed down through generations. These practices include traditional dances, songs, storytelling, and rituals. Visitors can witness and participate in these cultural performances, gaining insight into the history, beliefs, and customs of the local communities.
- Farming and Livelihoods: Agriculture is an essential aspect of the local communities’ livelihoods in and around Bwindi. The cultivation of crops such as bananas, beans, maize, and yams play a significant role in their subsistence. Visitors can learn about traditional farming methods, engage in farming activities, and gain an understanding of the vital link between culture, livelihoods, and the surrounding environment.
- Crafts and Artistry: The communities in the Bwindi region are known for their craftsmanship and artistic skills. They create intricate handwoven baskets, traditional pottery, wood carvings, and vibrant textiles. These crafts serve as a means of preserving cultural heritage, and visitors can explore local markets and workshops to appreciate and purchase these unique creations.
- Traditional Medicine: The local communities possess a wealth of traditional knowledge about medicinal plants found in the forest. They have a deep understanding of the healing properties and uses of various plants, which are often passed down through oral traditions. Visitors can learn about these traditional healing practices and the significance of medicinal plants in the local culture.
- Conservation and Community Engagement: Bwindi Impenetrable National Park has implemented community-based conservation initiatives that aim to engage and empower local communities. These efforts involve revenue-sharing programs, employment opportunities, and capacity-building initiatives. By involving communities in conservation activities, Bwindi strives to create a sustainable model that protects the environment while benefiting the people who call it home.