Community-based ecotourism:
Community-based ecotourism in Mount Mgahinga National Park offers a unique opportunity to
engage local communities in sustainable tourism practices while preserving the park’s natural and
cultural heritage. Here’s how community-based ecotourism can be implemented specifically in
Mount Mgahinga National Park:
Community-owned accommodations: Local communities residing near the park can establish and
manage eco-lodges, guesthouses, or homestays within the park or its vicinity. This allows visitors to
experience the rich cultural traditions and warm hospitality of the local communities while creating
direct economic benefits through employment and income generation.
Community-led trekking and guiding: Trained community members can serve as local guides, leading visitors on guided treks through the park &’s stunning landscapes and unique ecosystems. These guides can share their in-depth knowledge about the park’s flora, fauna, and cultural significance, enhancing the visitor experience while generating income for the community.
Cultural immersion experiences: Visitors can engage in cultural exchanges and immersive
experiences organized by local communities. This can include participating in traditional dances,
storytelling sessions, and crafts workshops, providing visitors with a deeper understanding of the
local culture and fostering an appreciation for the communities way of life.
Sustainable agriculture and agroforestry: Encouraging sustainable agricultural practices and
agroforestry initiatives can help improve the livelihoods of local communities while promoting
environmental conservation. Supporting community-led projects that focus on organic farming, tree
planting and sustainable land use can reduce the dependence on forest resources and mitigate
human-wildlife conflicts.
Conservation education and awareness: Implementing educational programs and workshops in local schools and communities can raise awareness about the importance of conservation and sustainable resource management. This can include teaching about the park’s biodiversity, climate change, and the role of communities in preserving the natural environment.
Community-based handicrafts and local products: Empowering local artisans and entrepreneurs to create and sell traditional handicrafts and locally sourced products can contribute to the economic
well-being of communities. Visitors can purchase these crafts as souvenirs, supporting sustainable
livelihoods and cultural preservation.
Community-led forest patrols: Engaging local community members in park patrols and wildlife
monitoring can enhance the protection of the park’s resources. This collaborative approach strengthens the relationship between communities and park management, promoting a sense of
ownership and responsibility for conservation efforts.
Successful implementation of community-based ecotourism in Mount Mgahinga National Park
requires strong partnerships between local communities, park management authorities, NGOs, and tourism operators. By involving local communities in decision-making processes and ensuring
equitable distribution of benefits, community-based ecotourism can become a powerful tool for
sustainable development, conservation, and cultural preservation in Mount Mgahinga National Park.
Environmental education and awareness:
Environmental education and awareness play a crucial role in promoting conservation and
sustainable practices in Mount Mgahinga National Park.
Here are some ways in which environmental education and awareness initiatives can be implemented in the park:
School programs: Collaborating with local schools, educational programs can be developed to teach
students about the importance of environmental conservation, biodiversity, and sustainable resource management. This can involve workshops, field trips to the park, and interactive sessions that encourage students to actively engage with environmental issues.
Community workshops and seminars: Conducting workshops and seminars in nearby villages and
communities can raise awareness about environmental challenges and solutions. These sessions can
cover topics such as waste management, sustainable agriculture, climate change, and the importance of protecting wildlife and their habitats.
Interpretive centers and signage: Establishing interpretive centers within the park or at key entry
points can provide visitors with educational displays, exhibits, and information about the park’s
ecosystems, biodiversity, and conservation efforts. Additionally, installing informative signage along
trails and significant sites can help visitors understand the importance of conservation and
sustainable practices.
Guided nature walks and talks: Offering guided nature walks and talks led by knowledgeable guides
can provide visitors with valuable insights into the park’s ecology and conservation efforts. Guides
can share information about the park’s flora, fauna, and conservation challenges, helping visitors
develop a deeper appreciation for the natural environment.
Outreach programs: Organizing outreach programs in nearby communities can involve activities such as tree-planting campaigns, clean-up drives, and wildlife monitoring initiatives. These programs aim to actively involve local communities in environmental conservation efforts and foster a sense of ownership and responsibility towards the park’s resources.
Public awareness campaigns: Utilizing various media platforms, including radio, television, and social media, public awareness campaigns can be launched to reach a wider audience. These campaigns
can highlight the importance of conservation, sustainable practices, and the role of local
communities in preserving the park’s natural and cultural heritage.
Collaboration with local stakeholders: Partnering with local community leaders, organizations, and stakeholders is essential for the success of environmental education and awareness initiatives.
Collaborative efforts can help tailor programs to the specific needs and interests of the local
communities, ensuring their active participation and long-term commitment to conservation.
By fostering environmental education and awareness in Mount Mgahinga National Park, local
communities, visitors, and stakeholders can develop a deeper understanding of the park’s ecological significance and their role in protecting its resources. These initiatives contribute to building a more
sustainable future for the park and its surrounding communities.
Agroforestry and sustainable agriculture Agroforestry and sustainable agriculture practices can
contribute to both environmental conservation and the economic well-being of local communities in
Mount Mgahinga National Park. Here are some ways in which agroforestry and sustainable
agriculture can be implemented:
Agroforestry systems: Encouraging the adoption of agroforestry systems among local farmers can
help improve land productivity, biodiversity conservation, and climate resilience. Agroforestry
combines the cultivation of crops with the planting of trees, allowing for multiple benefits such as
soil erosion control, shade provision, improved water retention, and diversification of income
sources.
Organic farming: Promoting organic farming methods reduces the reliance on synthetic fertilizers and
pesticides, minimizing the negative environmental impacts on the park’s ecosystems. Providing
training and resources to local farmers on organic farming techniques, composting, and natural pest
control methods can enhance soil fertility, protect water quality, and promote the production of
healthy and sustainable food.
Sustainable land management: Implementing sustainable land management practices, such as
contour plowing, terracing, and cover cropping, can help prevent soil erosion and maintain soil
health. These practices enable farmers to cultivate their land while minimizing the negative impacts
on natural resources and the surrounding ecosystem.
Alternative livelihoods: Supporting local communities in diversifying their income sources beyond
agriculture can help reduce pressure on the park’s resources. This can involve promoting alternative
livelihoods such as beekeeping, mushroom cultivation, or handicraft production, which can generate income while maintaining the ecological integrity of the park.
Community seed banks: Establishing community seed banks can help preserve local crop varieties
and promote seed exchange among farmers. This contributes to maintaining agrobiodiversity and
resilience to changing environmental conditions while ensuring access to diverse and locally adapted
plant genetic resources.
Training and capacity building: Providing training and capacity-building programs on sustainable
agriculture and agroforestry practices can empower local farmers with the necessary skills and
knowledge. This includes educating farmers on soil conservation, water management, organic
farming techniques, and the sustainable use of forest resources.
Market access and value chains: Assisting local farmers in accessing fair markets and establishing
sustainable value chains can create economic opportunities and enhance the viability of sustainable
agriculture practices. This can involve connecting farmers to eco-friendly and ethical market outlets,
supporting the certification of organic produce, and facilitating partnerships with local businesses
and tourism operators.
By promoting agroforestry and sustainable agriculture practices, Mount Mgahinga National Park can
support local communities in achieving food security, income generation, and environmental
conservation. These practices contribute to the long-term sustainability of the park and its
surrounding areas.
Community-based ecotourism:
Community-based ecotourism in Mount Mgahinga National Park offers a unique opportunity to
engage local communities in sustainable tourism practices while preserving the park’s natural and
cultural heritage. Here’s how community-based ecotourism can be implemented specifically in
Mount Mgahinga National Park:
Community-owned accommodations: Local communities residing near the park can establish and
manage eco-lodges, guesthouses, or homestays within the park or its vicinity. This allows visitors to
experience the rich cultural traditions and warm hospitality of the local communities while creating
direct economic benefits through employment and income generation.
Community-led trekking and guiding: Trained community members can serve as local guides, leading visitors on guided treks through the park &’s stunning landscapes and unique ecosystems. These guides can share their in-depth knowledge about the park’s flora, fauna, and cultural significance, enhancing the visitor experience while generating income for the community.
Cultural immersion experiences: Visitors can engage in cultural exchanges and immersive
experiences organized by local communities. This can include participating in traditional dances,
storytelling sessions, and crafts workshops, providing visitors with a deeper understanding of the
local culture and fostering an appreciation for the communities way of life.
Sustainable agriculture and agroforestry: Encouraging sustainable agricultural practices and
agroforestry initiatives can help improve the livelihoods of local communities while promoting
environmental conservation. Supporting community-led projects that focus on organic farming, tree
planting and sustainable land use can reduce the dependence on forest resources and mitigate
human-wildlife conflicts.
Conservation education and awareness: Implementing educational programs and workshops in local schools and communities can raise awareness about the importance of conservation and sustainable resource management. This can include teaching about the park’s biodiversity, climate change, and the role of communities in preserving the natural environment.
Community-based handicrafts and local products: Empowering local artisans and entrepreneurs to create and sell traditional handicrafts and locally sourced products can contribute to the economic
well-being of communities. Visitors can purchase these crafts as souvenirs, supporting sustainable
livelihoods and cultural preservation.
Community-led forest patrols: Engaging local community members in park patrols and wildlife
monitoring can enhance the protection of the park’s resources. This collaborative approach strengthens the relationship between communities and park management, promoting a sense of
ownership and responsibility for conservation efforts.
Successful implementation of community-based ecotourism in Mount Mgahinga National Park
requires strong partnerships between local communities, park management authorities, NGOs, and tourism operators. By involving local communities in decision-making processes and ensuring
equitable distribution of benefits, community-based ecotourism can become a powerful tool for
sustainable development, conservation, and cultural preservation in Mount Mgahinga National Park.
Environmental education and awareness:
Environmental education and awareness play a crucial role in promoting conservation and
sustainable practices in Mount Mgahinga National Park.
Here are some ways in which environmental education and awareness initiatives can be implemented in the park:
School programs: Collaborating with local schools, educational programs can be developed to teach
students about the importance of environmental conservation, biodiversity, and sustainable resource management. This can involve workshops, field trips to the park, and interactive sessions that encourage students to actively engage with environmental issues.
Community workshops and seminars: Conducting workshops and seminars in nearby villages and
communities can raise awareness about environmental challenges and solutions. These sessions can
cover topics such as waste management, sustainable agriculture, climate change, and the importance of protecting wildlife and their habitats.
Interpretive centers and signage: Establishing interpretive centers within the park or at key entry
points can provide visitors with educational displays, exhibits, and information about the park’s
ecosystems, biodiversity, and conservation efforts. Additionally, installing informative signage along
trails and significant sites can help visitors understand the importance of conservation and
sustainable practices.
Guided nature walks and talks: Offering guided nature walks and talks led by knowledgeable guides
can provide visitors with valuable insights into the park’s ecology and conservation efforts. Guides
can share information about the park’s flora, fauna, and conservation challenges, helping visitors
develop a deeper appreciation for the natural environment.
Outreach programs: Organizing outreach programs in nearby communities can involve activities such as tree-planting campaigns, clean-up drives, and wildlife monitoring initiatives. These programs aim to actively involve local communities in environmental conservation efforts and foster a sense of ownership and responsibility towards the park’s resources.
Public awareness campaigns: Utilizing various media platforms, including radio, television, and social media, public awareness campaigns can be launched to reach a wider audience. These campaigns
can highlight the importance of conservation, sustainable practices, and the role of local
communities in preserving the park’s natural and cultural heritage.
Collaboration with local stakeholders: Partnering with local community leaders, organizations, and stakeholders is essential for the success of environmental education and awareness initiatives.
Collaborative efforts can help tailor programs to the specific needs and interests of the local
communities, ensuring their active participation and long-term commitment to conservation.
By fostering environmental education and awareness in Mount Mgahinga National Park, local
communities, visitors, and stakeholders can develop a deeper understanding of the park’s ecological significance and their role in protecting its resources. These initiatives contribute to building a more
sustainable future for the park and its surrounding communities.
Agroforestry and sustainable agriculture Agroforestry and sustainable agriculture practices can
contribute to both environmental conservation and the economic well-being of local communities in
Mount Mgahinga National Park. Here are some ways in which agroforestry and sustainable
agriculture can be implemented:
Agroforestry systems: Encouraging the adoption of agroforestry systems among local farmers can
help improve land productivity, biodiversity conservation, and climate resilience. Agroforestry
combines the cultivation of crops with the planting of trees, allowing for multiple benefits such as
soil erosion control, shade provision, improved water retention, and diversification of income
sources.
Organic farming: Promoting organic farming methods reduces the reliance on synthetic fertilizers and
pesticides, minimizing the negative environmental impacts on the park’s ecosystems. Providing
training and resources to local farmers on organic farming techniques, composting, and natural pest
control methods can enhance soil fertility, protect water quality, and promote the production of
healthy and sustainable food.
Sustainable land management: Implementing sustainable land management practices, such as
contour plowing, terracing, and cover cropping, can help prevent soil erosion and maintain soil
health. These practices enable farmers to cultivate their land while minimizing the negative impacts
on natural resources and the surrounding ecosystem.
Alternative livelihoods: Supporting local communities in diversifying their income sources beyond
agriculture can help reduce pressure on the park’s resources. This can involve promoting alternative
livelihoods such as beekeeping, mushroom cultivation, or handicraft production, which can generate income while maintaining the ecological integrity of the park.
Community seed banks: Establishing community seed banks can help preserve local crop varieties
and promote seed exchange among farmers. This contributes to maintaining agrobiodiversity and
resilience to changing environmental conditions while ensuring access to diverse and locally adapted
plant genetic resources.
Training and capacity building: Providing training and capacity-building programs on sustainable
agriculture and agroforestry practices can empower local farmers with the necessary skills and
knowledge. This includes educating farmers on soil conservation, water management, organic
farming techniques, and the sustainable use of forest resources.
Market access and value chains: Assisting local farmers in accessing fair markets and establishing
sustainable value chains can create economic opportunities and enhance the viability of sustainable
agriculture practices. This can involve connecting farmers to eco-friendly and ethical market outlets,
supporting the certification of organic produce, and facilitating partnerships with local businesses
and tourism operators.
By promoting agroforestry and sustainable agriculture practices, Mount Mgahinga National Park can
support local communities in achieving food security, income generation, and environmental
conservation. These practices contribute to the long-term sustainability of the park and its
surrounding areas.
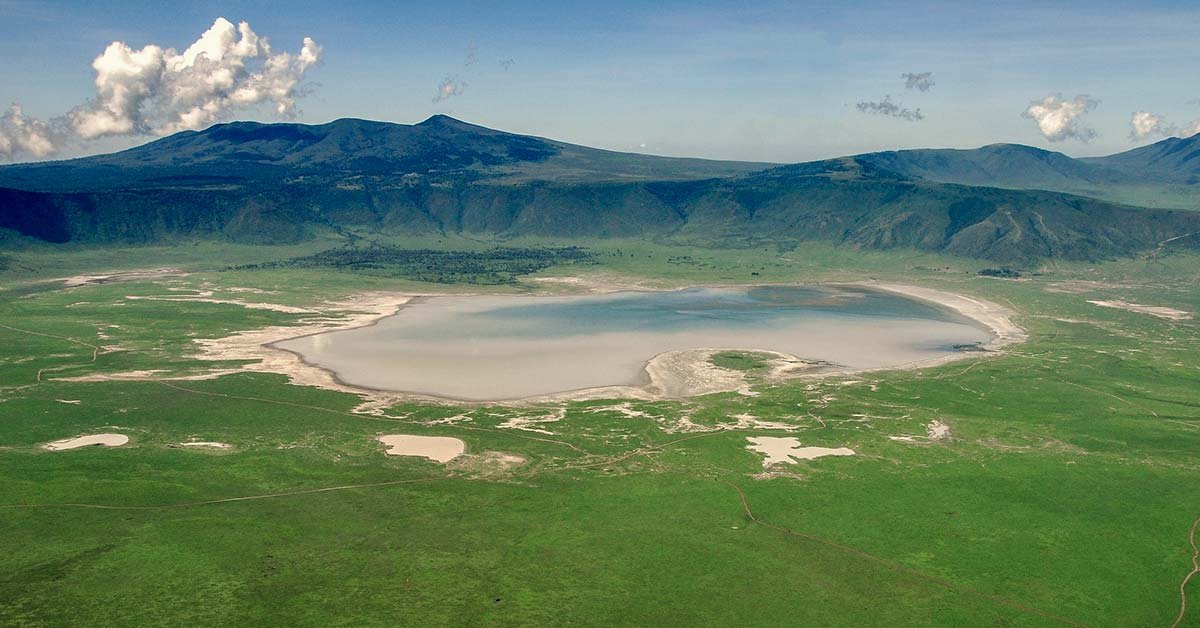
Mount Mgahinga National Park is a haven of natural beauty, rich cultural heritage, and diverse ecosystems. To preserve this unique environment while uplifting local communities, the implementation of community-based ecotourism, environmental education, awareness initiatives, and sustainable agriculture practices play a pivotal role.Fostering Sustainable Development and Conservation
This article explores how these approaches can be integrated, highlighting the benefits they offer for both conservation and the well-being of the communities surrounding the park. By fostering partnerships, empowering local communities, and raising awareness, Mount Mgahinga National Park can become a model for sustainable development and environmental stewardship.
 Community-based ecotourism:
Community-based ecotourism in Mount Mgahinga National Park offers a unique opportunity to
engage local communities in sustainable tourism practices while preserving the park’s natural and
cultural heritage. Here’s how community-based ecotourism can be implemented specifically in
Mount Mgahinga National Park:
Community-owned accommodations: Local communities residing near the park can establish and
manage eco-lodges, guesthouses, or homestays within the park or its vicinity. This allows visitors to
experience the rich cultural traditions and warm hospitality of the local communities while creating
direct economic benefits through employment and income generation.
Community-led trekking and guiding: Trained community members can serve as local guides, leading visitors on guided treks through the park &’s stunning landscapes and unique ecosystems. These guides can share their in-depth knowledge about the park’s flora, fauna, and cultural significance, enhancing the visitor experience while generating income for the community.
Cultural immersion experiences: Visitors can engage in cultural exchanges and immersive
experiences organized by local communities. This can include participating in traditional dances,
storytelling sessions, and crafts workshops, providing visitors with a deeper understanding of the
local culture and fostering an appreciation for the communities way of life.
Sustainable agriculture and agroforestry: Encouraging sustainable agricultural practices and
agroforestry initiatives can help improve the livelihoods of local communities while promoting
environmental conservation. Supporting community-led projects that focus on organic farming, tree
planting and sustainable land use can reduce the dependence on forest resources and mitigate
human-wildlife conflicts.
Conservation education and awareness: Implementing educational programs and workshops in local schools and communities can raise awareness about the importance of conservation and sustainable resource management. This can include teaching about the park’s biodiversity, climate change, and the role of communities in preserving the natural environment.
Community-based handicrafts and local products: Empowering local artisans and entrepreneurs to create and sell traditional handicrafts and locally sourced products can contribute to the economic
well-being of communities. Visitors can purchase these crafts as souvenirs, supporting sustainable
livelihoods and cultural preservation.
Community-led forest patrols: Engaging local community members in park patrols and wildlife
monitoring can enhance the protection of the park’s resources. This collaborative approach strengthens the relationship between communities and park management, promoting a sense of
ownership and responsibility for conservation efforts.
Successful implementation of community-based ecotourism in Mount Mgahinga National Park
requires strong partnerships between local communities, park management authorities, NGOs, and tourism operators. By involving local communities in decision-making processes and ensuring
equitable distribution of benefits, community-based ecotourism can become a powerful tool for
sustainable development, conservation, and cultural preservation in Mount Mgahinga National Park.
Environmental education and awareness:
Environmental education and awareness play a crucial role in promoting conservation and
sustainable practices in Mount Mgahinga National Park.
Here are some ways in which environmental education and awareness initiatives can be implemented in the park:
School programs: Collaborating with local schools, educational programs can be developed to teach
students about the importance of environmental conservation, biodiversity, and sustainable resource management. This can involve workshops, field trips to the park, and interactive sessions that encourage students to actively engage with environmental issues.
Community workshops and seminars: Conducting workshops and seminars in nearby villages and
communities can raise awareness about environmental challenges and solutions. These sessions can
cover topics such as waste management, sustainable agriculture, climate change, and the importance of protecting wildlife and their habitats.
Interpretive centers and signage: Establishing interpretive centers within the park or at key entry
points can provide visitors with educational displays, exhibits, and information about the park’s
ecosystems, biodiversity, and conservation efforts. Additionally, installing informative signage along
trails and significant sites can help visitors understand the importance of conservation and
sustainable practices.
Guided nature walks and talks: Offering guided nature walks and talks led by knowledgeable guides
can provide visitors with valuable insights into the park’s ecology and conservation efforts. Guides
can share information about the park’s flora, fauna, and conservation challenges, helping visitors
develop a deeper appreciation for the natural environment.
Outreach programs: Organizing outreach programs in nearby communities can involve activities such as tree-planting campaigns, clean-up drives, and wildlife monitoring initiatives. These programs aim to actively involve local communities in environmental conservation efforts and foster a sense of ownership and responsibility towards the park’s resources.
Public awareness campaigns: Utilizing various media platforms, including radio, television, and social media, public awareness campaigns can be launched to reach a wider audience. These campaigns
can highlight the importance of conservation, sustainable practices, and the role of local
communities in preserving the park’s natural and cultural heritage.
Collaboration with local stakeholders: Partnering with local community leaders, organizations, and stakeholders is essential for the success of environmental education and awareness initiatives.
Collaborative efforts can help tailor programs to the specific needs and interests of the local
communities, ensuring their active participation and long-term commitment to conservation.
By fostering environmental education and awareness in Mount Mgahinga National Park, local
communities, visitors, and stakeholders can develop a deeper understanding of the park’s ecological significance and their role in protecting its resources. These initiatives contribute to building a more
sustainable future for the park and its surrounding communities.
Agroforestry and sustainable agriculture Agroforestry and sustainable agriculture practices can
contribute to both environmental conservation and the economic well-being of local communities in
Mount Mgahinga National Park. Here are some ways in which agroforestry and sustainable
agriculture can be implemented:
Agroforestry systems: Encouraging the adoption of agroforestry systems among local farmers can
help improve land productivity, biodiversity conservation, and climate resilience. Agroforestry
combines the cultivation of crops with the planting of trees, allowing for multiple benefits such as
soil erosion control, shade provision, improved water retention, and diversification of income
sources.
Organic farming: Promoting organic farming methods reduces the reliance on synthetic fertilizers and
pesticides, minimizing the negative environmental impacts on the park’s ecosystems. Providing
training and resources to local farmers on organic farming techniques, composting, and natural pest
control methods can enhance soil fertility, protect water quality, and promote the production of
healthy and sustainable food.
Sustainable land management: Implementing sustainable land management practices, such as
contour plowing, terracing, and cover cropping, can help prevent soil erosion and maintain soil
health. These practices enable farmers to cultivate their land while minimizing the negative impacts
on natural resources and the surrounding ecosystem.
Alternative livelihoods: Supporting local communities in diversifying their income sources beyond
agriculture can help reduce pressure on the park’s resources. This can involve promoting alternative
livelihoods such as beekeeping, mushroom cultivation, or handicraft production, which can generate income while maintaining the ecological integrity of the park.
Community seed banks: Establishing community seed banks can help preserve local crop varieties
and promote seed exchange among farmers. This contributes to maintaining agrobiodiversity and
resilience to changing environmental conditions while ensuring access to diverse and locally adapted
plant genetic resources.
Training and capacity building: Providing training and capacity-building programs on sustainable
agriculture and agroforestry practices can empower local farmers with the necessary skills and
knowledge. This includes educating farmers on soil conservation, water management, organic
farming techniques, and the sustainable use of forest resources.
Market access and value chains: Assisting local farmers in accessing fair markets and establishing
sustainable value chains can create economic opportunities and enhance the viability of sustainable
agriculture practices. This can involve connecting farmers to eco-friendly and ethical market outlets,
supporting the certification of organic produce, and facilitating partnerships with local businesses
and tourism operators.
By promoting agroforestry and sustainable agriculture practices, Mount Mgahinga National Park can
support local communities in achieving food security, income generation, and environmental
conservation. These practices contribute to the long-term sustainability of the park and its
surrounding areas.
Community-based ecotourism:
Community-based ecotourism in Mount Mgahinga National Park offers a unique opportunity to
engage local communities in sustainable tourism practices while preserving the park’s natural and
cultural heritage. Here’s how community-based ecotourism can be implemented specifically in
Mount Mgahinga National Park:
Community-owned accommodations: Local communities residing near the park can establish and
manage eco-lodges, guesthouses, or homestays within the park or its vicinity. This allows visitors to
experience the rich cultural traditions and warm hospitality of the local communities while creating
direct economic benefits through employment and income generation.
Community-led trekking and guiding: Trained community members can serve as local guides, leading visitors on guided treks through the park &’s stunning landscapes and unique ecosystems. These guides can share their in-depth knowledge about the park’s flora, fauna, and cultural significance, enhancing the visitor experience while generating income for the community.
Cultural immersion experiences: Visitors can engage in cultural exchanges and immersive
experiences organized by local communities. This can include participating in traditional dances,
storytelling sessions, and crafts workshops, providing visitors with a deeper understanding of the
local culture and fostering an appreciation for the communities way of life.
Sustainable agriculture and agroforestry: Encouraging sustainable agricultural practices and
agroforestry initiatives can help improve the livelihoods of local communities while promoting
environmental conservation. Supporting community-led projects that focus on organic farming, tree
planting and sustainable land use can reduce the dependence on forest resources and mitigate
human-wildlife conflicts.
Conservation education and awareness: Implementing educational programs and workshops in local schools and communities can raise awareness about the importance of conservation and sustainable resource management. This can include teaching about the park’s biodiversity, climate change, and the role of communities in preserving the natural environment.
Community-based handicrafts and local products: Empowering local artisans and entrepreneurs to create and sell traditional handicrafts and locally sourced products can contribute to the economic
well-being of communities. Visitors can purchase these crafts as souvenirs, supporting sustainable
livelihoods and cultural preservation.
Community-led forest patrols: Engaging local community members in park patrols and wildlife
monitoring can enhance the protection of the park’s resources. This collaborative approach strengthens the relationship between communities and park management, promoting a sense of
ownership and responsibility for conservation efforts.
Successful implementation of community-based ecotourism in Mount Mgahinga National Park
requires strong partnerships between local communities, park management authorities, NGOs, and tourism operators. By involving local communities in decision-making processes and ensuring
equitable distribution of benefits, community-based ecotourism can become a powerful tool for
sustainable development, conservation, and cultural preservation in Mount Mgahinga National Park.
Environmental education and awareness:
Environmental education and awareness play a crucial role in promoting conservation and
sustainable practices in Mount Mgahinga National Park.
Here are some ways in which environmental education and awareness initiatives can be implemented in the park:
School programs: Collaborating with local schools, educational programs can be developed to teach
students about the importance of environmental conservation, biodiversity, and sustainable resource management. This can involve workshops, field trips to the park, and interactive sessions that encourage students to actively engage with environmental issues.
Community workshops and seminars: Conducting workshops and seminars in nearby villages and
communities can raise awareness about environmental challenges and solutions. These sessions can
cover topics such as waste management, sustainable agriculture, climate change, and the importance of protecting wildlife and their habitats.
Interpretive centers and signage: Establishing interpretive centers within the park or at key entry
points can provide visitors with educational displays, exhibits, and information about the park’s
ecosystems, biodiversity, and conservation efforts. Additionally, installing informative signage along
trails and significant sites can help visitors understand the importance of conservation and
sustainable practices.
Guided nature walks and talks: Offering guided nature walks and talks led by knowledgeable guides
can provide visitors with valuable insights into the park’s ecology and conservation efforts. Guides
can share information about the park’s flora, fauna, and conservation challenges, helping visitors
develop a deeper appreciation for the natural environment.
Outreach programs: Organizing outreach programs in nearby communities can involve activities such as tree-planting campaigns, clean-up drives, and wildlife monitoring initiatives. These programs aim to actively involve local communities in environmental conservation efforts and foster a sense of ownership and responsibility towards the park’s resources.
Public awareness campaigns: Utilizing various media platforms, including radio, television, and social media, public awareness campaigns can be launched to reach a wider audience. These campaigns
can highlight the importance of conservation, sustainable practices, and the role of local
communities in preserving the park’s natural and cultural heritage.
Collaboration with local stakeholders: Partnering with local community leaders, organizations, and stakeholders is essential for the success of environmental education and awareness initiatives.
Collaborative efforts can help tailor programs to the specific needs and interests of the local
communities, ensuring their active participation and long-term commitment to conservation.
By fostering environmental education and awareness in Mount Mgahinga National Park, local
communities, visitors, and stakeholders can develop a deeper understanding of the park’s ecological significance and their role in protecting its resources. These initiatives contribute to building a more
sustainable future for the park and its surrounding communities.
Agroforestry and sustainable agriculture Agroforestry and sustainable agriculture practices can
contribute to both environmental conservation and the economic well-being of local communities in
Mount Mgahinga National Park. Here are some ways in which agroforestry and sustainable
agriculture can be implemented:
Agroforestry systems: Encouraging the adoption of agroforestry systems among local farmers can
help improve land productivity, biodiversity conservation, and climate resilience. Agroforestry
combines the cultivation of crops with the planting of trees, allowing for multiple benefits such as
soil erosion control, shade provision, improved water retention, and diversification of income
sources.
Organic farming: Promoting organic farming methods reduces the reliance on synthetic fertilizers and
pesticides, minimizing the negative environmental impacts on the park’s ecosystems. Providing
training and resources to local farmers on organic farming techniques, composting, and natural pest
control methods can enhance soil fertility, protect water quality, and promote the production of
healthy and sustainable food.
Sustainable land management: Implementing sustainable land management practices, such as
contour plowing, terracing, and cover cropping, can help prevent soil erosion and maintain soil
health. These practices enable farmers to cultivate their land while minimizing the negative impacts
on natural resources and the surrounding ecosystem.
Alternative livelihoods: Supporting local communities in diversifying their income sources beyond
agriculture can help reduce pressure on the park’s resources. This can involve promoting alternative
livelihoods such as beekeeping, mushroom cultivation, or handicraft production, which can generate income while maintaining the ecological integrity of the park.
Community seed banks: Establishing community seed banks can help preserve local crop varieties
and promote seed exchange among farmers. This contributes to maintaining agrobiodiversity and
resilience to changing environmental conditions while ensuring access to diverse and locally adapted
plant genetic resources.
Training and capacity building: Providing training and capacity-building programs on sustainable
agriculture and agroforestry practices can empower local farmers with the necessary skills and
knowledge. This includes educating farmers on soil conservation, water management, organic
farming techniques, and the sustainable use of forest resources.
Market access and value chains: Assisting local farmers in accessing fair markets and establishing
sustainable value chains can create economic opportunities and enhance the viability of sustainable
agriculture practices. This can involve connecting farmers to eco-friendly and ethical market outlets,
supporting the certification of organic produce, and facilitating partnerships with local businesses
and tourism operators.
By promoting agroforestry and sustainable agriculture practices, Mount Mgahinga National Park can
support local communities in achieving food security, income generation, and environmental
conservation. These practices contribute to the long-term sustainability of the park and its
surrounding areas.
 Community-based ecotourism:
Community-based ecotourism in Mount Mgahinga National Park offers a unique opportunity to
engage local communities in sustainable tourism practices while preserving the park’s natural and
cultural heritage. Here’s how community-based ecotourism can be implemented specifically in
Mount Mgahinga National Park:
Community-owned accommodations: Local communities residing near the park can establish and
manage eco-lodges, guesthouses, or homestays within the park or its vicinity. This allows visitors to
experience the rich cultural traditions and warm hospitality of the local communities while creating
direct economic benefits through employment and income generation.
Community-led trekking and guiding: Trained community members can serve as local guides, leading visitors on guided treks through the park &’s stunning landscapes and unique ecosystems. These guides can share their in-depth knowledge about the park’s flora, fauna, and cultural significance, enhancing the visitor experience while generating income for the community.
Cultural immersion experiences: Visitors can engage in cultural exchanges and immersive
experiences organized by local communities. This can include participating in traditional dances,
storytelling sessions, and crafts workshops, providing visitors with a deeper understanding of the
local culture and fostering an appreciation for the communities way of life.
Sustainable agriculture and agroforestry: Encouraging sustainable agricultural practices and
agroforestry initiatives can help improve the livelihoods of local communities while promoting
environmental conservation. Supporting community-led projects that focus on organic farming, tree
planting and sustainable land use can reduce the dependence on forest resources and mitigate
human-wildlife conflicts.
Conservation education and awareness: Implementing educational programs and workshops in local schools and communities can raise awareness about the importance of conservation and sustainable resource management. This can include teaching about the park’s biodiversity, climate change, and the role of communities in preserving the natural environment.
Community-based handicrafts and local products: Empowering local artisans and entrepreneurs to create and sell traditional handicrafts and locally sourced products can contribute to the economic
well-being of communities. Visitors can purchase these crafts as souvenirs, supporting sustainable
livelihoods and cultural preservation.
Community-led forest patrols: Engaging local community members in park patrols and wildlife
monitoring can enhance the protection of the park’s resources. This collaborative approach strengthens the relationship between communities and park management, promoting a sense of
ownership and responsibility for conservation efforts.
Successful implementation of community-based ecotourism in Mount Mgahinga National Park
requires strong partnerships between local communities, park management authorities, NGOs, and tourism operators. By involving local communities in decision-making processes and ensuring
equitable distribution of benefits, community-based ecotourism can become a powerful tool for
sustainable development, conservation, and cultural preservation in Mount Mgahinga National Park.
Environmental education and awareness:
Environmental education and awareness play a crucial role in promoting conservation and
sustainable practices in Mount Mgahinga National Park.
Here are some ways in which environmental education and awareness initiatives can be implemented in the park:
School programs: Collaborating with local schools, educational programs can be developed to teach
students about the importance of environmental conservation, biodiversity, and sustainable resource management. This can involve workshops, field trips to the park, and interactive sessions that encourage students to actively engage with environmental issues.
Community workshops and seminars: Conducting workshops and seminars in nearby villages and
communities can raise awareness about environmental challenges and solutions. These sessions can
cover topics such as waste management, sustainable agriculture, climate change, and the importance of protecting wildlife and their habitats.
Interpretive centers and signage: Establishing interpretive centers within the park or at key entry
points can provide visitors with educational displays, exhibits, and information about the park’s
ecosystems, biodiversity, and conservation efforts. Additionally, installing informative signage along
trails and significant sites can help visitors understand the importance of conservation and
sustainable practices.
Guided nature walks and talks: Offering guided nature walks and talks led by knowledgeable guides
can provide visitors with valuable insights into the park’s ecology and conservation efforts. Guides
can share information about the park’s flora, fauna, and conservation challenges, helping visitors
develop a deeper appreciation for the natural environment.
Outreach programs: Organizing outreach programs in nearby communities can involve activities such as tree-planting campaigns, clean-up drives, and wildlife monitoring initiatives. These programs aim to actively involve local communities in environmental conservation efforts and foster a sense of ownership and responsibility towards the park’s resources.
Public awareness campaigns: Utilizing various media platforms, including radio, television, and social media, public awareness campaigns can be launched to reach a wider audience. These campaigns
can highlight the importance of conservation, sustainable practices, and the role of local
communities in preserving the park’s natural and cultural heritage.
Collaboration with local stakeholders: Partnering with local community leaders, organizations, and stakeholders is essential for the success of environmental education and awareness initiatives.
Collaborative efforts can help tailor programs to the specific needs and interests of the local
communities, ensuring their active participation and long-term commitment to conservation.
By fostering environmental education and awareness in Mount Mgahinga National Park, local
communities, visitors, and stakeholders can develop a deeper understanding of the park’s ecological significance and their role in protecting its resources. These initiatives contribute to building a more
sustainable future for the park and its surrounding communities.
Agroforestry and sustainable agriculture Agroforestry and sustainable agriculture practices can
contribute to both environmental conservation and the economic well-being of local communities in
Mount Mgahinga National Park. Here are some ways in which agroforestry and sustainable
agriculture can be implemented:
Agroforestry systems: Encouraging the adoption of agroforestry systems among local farmers can
help improve land productivity, biodiversity conservation, and climate resilience. Agroforestry
combines the cultivation of crops with the planting of trees, allowing for multiple benefits such as
soil erosion control, shade provision, improved water retention, and diversification of income
sources.
Organic farming: Promoting organic farming methods reduces the reliance on synthetic fertilizers and
pesticides, minimizing the negative environmental impacts on the park’s ecosystems. Providing
training and resources to local farmers on organic farming techniques, composting, and natural pest
control methods can enhance soil fertility, protect water quality, and promote the production of
healthy and sustainable food.
Sustainable land management: Implementing sustainable land management practices, such as
contour plowing, terracing, and cover cropping, can help prevent soil erosion and maintain soil
health. These practices enable farmers to cultivate their land while minimizing the negative impacts
on natural resources and the surrounding ecosystem.
Alternative livelihoods: Supporting local communities in diversifying their income sources beyond
agriculture can help reduce pressure on the park’s resources. This can involve promoting alternative
livelihoods such as beekeeping, mushroom cultivation, or handicraft production, which can generate income while maintaining the ecological integrity of the park.
Community seed banks: Establishing community seed banks can help preserve local crop varieties
and promote seed exchange among farmers. This contributes to maintaining agrobiodiversity and
resilience to changing environmental conditions while ensuring access to diverse and locally adapted
plant genetic resources.
Training and capacity building: Providing training and capacity-building programs on sustainable
agriculture and agroforestry practices can empower local farmers with the necessary skills and
knowledge. This includes educating farmers on soil conservation, water management, organic
farming techniques, and the sustainable use of forest resources.
Market access and value chains: Assisting local farmers in accessing fair markets and establishing
sustainable value chains can create economic opportunities and enhance the viability of sustainable
agriculture practices. This can involve connecting farmers to eco-friendly and ethical market outlets,
supporting the certification of organic produce, and facilitating partnerships with local businesses
and tourism operators.
By promoting agroforestry and sustainable agriculture practices, Mount Mgahinga National Park can
support local communities in achieving food security, income generation, and environmental
conservation. These practices contribute to the long-term sustainability of the park and its
surrounding areas.
Community-based ecotourism:
Community-based ecotourism in Mount Mgahinga National Park offers a unique opportunity to
engage local communities in sustainable tourism practices while preserving the park’s natural and
cultural heritage. Here’s how community-based ecotourism can be implemented specifically in
Mount Mgahinga National Park:
Community-owned accommodations: Local communities residing near the park can establish and
manage eco-lodges, guesthouses, or homestays within the park or its vicinity. This allows visitors to
experience the rich cultural traditions and warm hospitality of the local communities while creating
direct economic benefits through employment and income generation.
Community-led trekking and guiding: Trained community members can serve as local guides, leading visitors on guided treks through the park &’s stunning landscapes and unique ecosystems. These guides can share their in-depth knowledge about the park’s flora, fauna, and cultural significance, enhancing the visitor experience while generating income for the community.
Cultural immersion experiences: Visitors can engage in cultural exchanges and immersive
experiences organized by local communities. This can include participating in traditional dances,
storytelling sessions, and crafts workshops, providing visitors with a deeper understanding of the
local culture and fostering an appreciation for the communities way of life.
Sustainable agriculture and agroforestry: Encouraging sustainable agricultural practices and
agroforestry initiatives can help improve the livelihoods of local communities while promoting
environmental conservation. Supporting community-led projects that focus on organic farming, tree
planting and sustainable land use can reduce the dependence on forest resources and mitigate
human-wildlife conflicts.
Conservation education and awareness: Implementing educational programs and workshops in local schools and communities can raise awareness about the importance of conservation and sustainable resource management. This can include teaching about the park’s biodiversity, climate change, and the role of communities in preserving the natural environment.
Community-based handicrafts and local products: Empowering local artisans and entrepreneurs to create and sell traditional handicrafts and locally sourced products can contribute to the economic
well-being of communities. Visitors can purchase these crafts as souvenirs, supporting sustainable
livelihoods and cultural preservation.
Community-led forest patrols: Engaging local community members in park patrols and wildlife
monitoring can enhance the protection of the park’s resources. This collaborative approach strengthens the relationship between communities and park management, promoting a sense of
ownership and responsibility for conservation efforts.
Successful implementation of community-based ecotourism in Mount Mgahinga National Park
requires strong partnerships between local communities, park management authorities, NGOs, and tourism operators. By involving local communities in decision-making processes and ensuring
equitable distribution of benefits, community-based ecotourism can become a powerful tool for
sustainable development, conservation, and cultural preservation in Mount Mgahinga National Park.
Environmental education and awareness:
Environmental education and awareness play a crucial role in promoting conservation and
sustainable practices in Mount Mgahinga National Park.
Here are some ways in which environmental education and awareness initiatives can be implemented in the park:
School programs: Collaborating with local schools, educational programs can be developed to teach
students about the importance of environmental conservation, biodiversity, and sustainable resource management. This can involve workshops, field trips to the park, and interactive sessions that encourage students to actively engage with environmental issues.
Community workshops and seminars: Conducting workshops and seminars in nearby villages and
communities can raise awareness about environmental challenges and solutions. These sessions can
cover topics such as waste management, sustainable agriculture, climate change, and the importance of protecting wildlife and their habitats.
Interpretive centers and signage: Establishing interpretive centers within the park or at key entry
points can provide visitors with educational displays, exhibits, and information about the park’s
ecosystems, biodiversity, and conservation efforts. Additionally, installing informative signage along
trails and significant sites can help visitors understand the importance of conservation and
sustainable practices.
Guided nature walks and talks: Offering guided nature walks and talks led by knowledgeable guides
can provide visitors with valuable insights into the park’s ecology and conservation efforts. Guides
can share information about the park’s flora, fauna, and conservation challenges, helping visitors
develop a deeper appreciation for the natural environment.
Outreach programs: Organizing outreach programs in nearby communities can involve activities such as tree-planting campaigns, clean-up drives, and wildlife monitoring initiatives. These programs aim to actively involve local communities in environmental conservation efforts and foster a sense of ownership and responsibility towards the park’s resources.
Public awareness campaigns: Utilizing various media platforms, including radio, television, and social media, public awareness campaigns can be launched to reach a wider audience. These campaigns
can highlight the importance of conservation, sustainable practices, and the role of local
communities in preserving the park’s natural and cultural heritage.
Collaboration with local stakeholders: Partnering with local community leaders, organizations, and stakeholders is essential for the success of environmental education and awareness initiatives.
Collaborative efforts can help tailor programs to the specific needs and interests of the local
communities, ensuring their active participation and long-term commitment to conservation.
By fostering environmental education and awareness in Mount Mgahinga National Park, local
communities, visitors, and stakeholders can develop a deeper understanding of the park’s ecological significance and their role in protecting its resources. These initiatives contribute to building a more
sustainable future for the park and its surrounding communities.
Agroforestry and sustainable agriculture Agroforestry and sustainable agriculture practices can
contribute to both environmental conservation and the economic well-being of local communities in
Mount Mgahinga National Park. Here are some ways in which agroforestry and sustainable
agriculture can be implemented:
Agroforestry systems: Encouraging the adoption of agroforestry systems among local farmers can
help improve land productivity, biodiversity conservation, and climate resilience. Agroforestry
combines the cultivation of crops with the planting of trees, allowing for multiple benefits such as
soil erosion control, shade provision, improved water retention, and diversification of income
sources.
Organic farming: Promoting organic farming methods reduces the reliance on synthetic fertilizers and
pesticides, minimizing the negative environmental impacts on the park’s ecosystems. Providing
training and resources to local farmers on organic farming techniques, composting, and natural pest
control methods can enhance soil fertility, protect water quality, and promote the production of
healthy and sustainable food.
Sustainable land management: Implementing sustainable land management practices, such as
contour plowing, terracing, and cover cropping, can help prevent soil erosion and maintain soil
health. These practices enable farmers to cultivate their land while minimizing the negative impacts
on natural resources and the surrounding ecosystem.
Alternative livelihoods: Supporting local communities in diversifying their income sources beyond
agriculture can help reduce pressure on the park’s resources. This can involve promoting alternative
livelihoods such as beekeeping, mushroom cultivation, or handicraft production, which can generate income while maintaining the ecological integrity of the park.
Community seed banks: Establishing community seed banks can help preserve local crop varieties
and promote seed exchange among farmers. This contributes to maintaining agrobiodiversity and
resilience to changing environmental conditions while ensuring access to diverse and locally adapted
plant genetic resources.
Training and capacity building: Providing training and capacity-building programs on sustainable
agriculture and agroforestry practices can empower local farmers with the necessary skills and
knowledge. This includes educating farmers on soil conservation, water management, organic
farming techniques, and the sustainable use of forest resources.
Market access and value chains: Assisting local farmers in accessing fair markets and establishing
sustainable value chains can create economic opportunities and enhance the viability of sustainable
agriculture practices. This can involve connecting farmers to eco-friendly and ethical market outlets,
supporting the certification of organic produce, and facilitating partnerships with local businesses
and tourism operators.
By promoting agroforestry and sustainable agriculture practices, Mount Mgahinga National Park can
support local communities in achieving food security, income generation, and environmental
conservation. These practices contribute to the long-term sustainability of the park and its
surrounding areas.